PIGMENTATION TREATMENT SURAT
Skin Pigmentation : Causes, Symptoms And Solutions
Observing a general darkening of the skin or dark patches on the face and body is a sign of skin pigmentation. This condition has both internal (genetic) and external causes and can affect individuals of any skin color, although it is more commonly seen in women. Those living in equatorial regions or with Asian heritage are more prone to pigmentation due to the sun’s exposure. Pigmentation issues can be more prominent in middle-aged people as some types of pigmentation are accelerated with aging.
What is Pigmentation?
Melanin, a pigment produced by melanocytes, gives color to our skin, hair, mucous membranes, and the retina of the eye. However, excess production of melanin can cause hyperpigmentation, leading to dark spots, patches or discoloration of the skin, resulting in uneven skin tone.
Hyperpigmentation usually affects specific areas of the skin, making them appear darker than usual. These patches can vary in size and appear anywhere on the body. To determine the exact cause of pigmentation, it is best to consult a dermatologist.

What Causes Skin Pigmentation?
Increased melanin production, from internal or external factors, can cause skin pigmentation disorders.
External Factors:
Sun exposure: Pigmentation can be caused by overexposure to UVA rays from the sun, which penetrate deep into the skin and stimulate the production of excess melanin.
Injury: An external injury, such as a cut, bruise, or pimple, can trigger an inflammatory reaction that leads to excess melanin production. Improper hair removal or depilatory cream can also cause this reaction.
Medication: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy and tetracycline antibiotics, can cause unwanted pigmentation as a side effect.
Allergies: Contact dermatitis resulting from the use of cosmetics, hair dyes and similar products can lead to pigmentation of the skin.
Internal Factors:
Hormonal fluctuations: Pigmentation, known as Melasma, results from hormonal imbalance caused by increased estrogen and progesterone levels due to pregnancy or birth control pills.
Hereditary: Hereditary factors can influence skin pigmentation, including lentigines which are linked to hereditary multisystemic syndromes.
Illness or disease: Certain medical conditions, such as Addison’s disease and other endocrine disorders, can disrupt hormonal levels and increase melanin production.
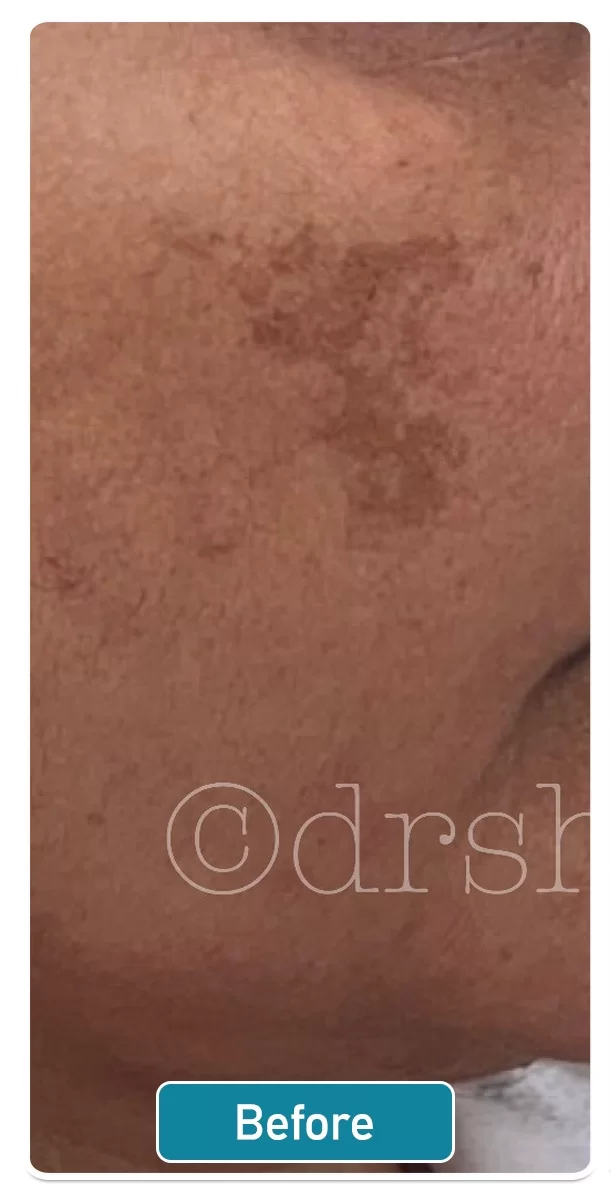
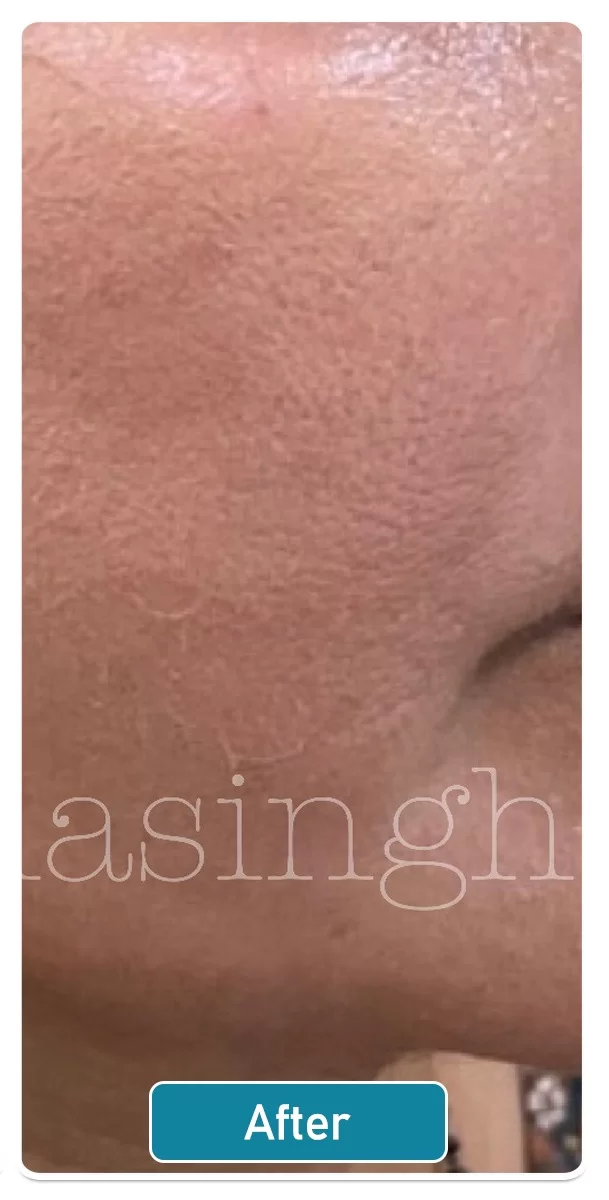
Pigmentation Symptoms
Common types of pigmentation include:
Freckles: Freckles are small, circular spots that appear on the skin due to frequent exposure to sunlight. They usually affect people with lighter skin tones and are commonly found on exposed areas such as the face. Hereditary factors can also contribute to their appearance.
Post: inflammatory pigmentation – This type of skin discoloration is often caused by injuries such as bruises, burns, friction, or harsh chemical treatments, and can also result from post-acne breakouts, leaving behind reddish, brown, or black marks.
Melasma: Melasma is a common skin condition that causes irregular brown to gray patches on the face, specifically on the cheeks, nose, and jawline, and is more prevalent in women.
Sunspots: These pigmentation spots, also known as solar lentigines, are caused by sun exposure and the amount of pigmentation depends on the extent of melanin pigment exposure to UV rays.
Diagnosis
Once the examination is complete, the dermatologist will recommend treatment options, which may include topical medication or advanced dermatological procedures tailored to treat the specific type of pigmentation.
Are You At Risk?
Pigmentation is a condition that can affect anyone, regardless of their skin type, age, gender, or geographical location, although it is more common among Asians. Exposure to the sun is a primary cause of pigmentation, and even a single day of sun exposure can damage the skin. Individuals with a hereditary tendency are more likely to develop pigmentation. Therefore, early diagnosis and timely intervention are crucial to effectively reverse the condition.
Prevention and Management
It’s important to always use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with the highest SPF that protects from both UVA and UVB rays of the sun. This will help prevent skin damage caused by sun exposure.
To protect your skin from environmental damage, pollutants, and dirt, follow a good skin care routine. It’s recommended to wear hats or scarves to avoid sun exposure during peak hours of sunlight.
Home Remedies
We do not recommend using home remedies as there is no scientific data to support them. In fact, they may even irritate the skin, making the treatment last longer. It’s important to seek medical intervention for appropriate treatments and results.
Treatment Options
There are various treatment options available for pigmentation on the skin. These options include topical medication, chemical peels, and laser therapy with Q-switched NdYAG lasers.
Prognosis
The prognosis for pigmentation is generally positive, but it’s important to treat it in a timely manner to avoid aggravation. While mild pigmentation can be treated with topical treatments, more severe cases require advanced treatments such as laser therapy. It is recommended to consult a dermatologist to determine the extent of pigmentation and the best treatment method for your specific case.
How To Get Started?
You can easily book an appointment online or over the phone by calling 62878 78787. Our customer care team will then schedule an appointment with a dermatologist at your preferred time and convenience.
make your appointment with
our skin specialist in Surat
Make Appointment FAQ
Why does skin pigmentation occur, and why is it more prevalent in women?
Skin pigmentation occurs as a result of excess production of melanin, caused by sun exposure, hormonal imbalances, injury, medication, or hereditary conditions. It is more prevalent in women because of the fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly during pregnancy or with the use of contraceptive pills.
Is pigmentation merely a cosmetic concern, or may it indicate an underlying condition?
Although pigmentation is usually cosmetic, on occasion it can reflect underlying diseases endocrine disease. That is why a full diagnosis by a dermatologist prior to commencing treatment is essential.
What are the most common forms of pigmentation treated in your clinic?
We treat various types of pigmentation such as freckles, melasma, sun spots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) due to acne, trauma, or skin treatments.
How is pigmentation diagnosed at Glamour Skin Studio?
Our dermatologist, Dr. Sheena Singh employ equipment such as derma scan analysis, thorough examination of the skin, review of medical history, and if required, skin biopsies to determine the cause and type of pigmentation.
Can pigmentation be prevented, and what skincare habits should I follow?
Yes, prevention is possible through the regular use of broad-spectrum SPF, the use of protective clothing, and a consistent skincare routine to protect against sun and environmental damage. Early diagnosis can prevent further worsening of pigmentation.

Best psychology & counseling to help you understand the problems.
Contact
© 2023 Glamour Skin Studio. All Rights Reserved.